By Heather Patrice Brown, Development Manager
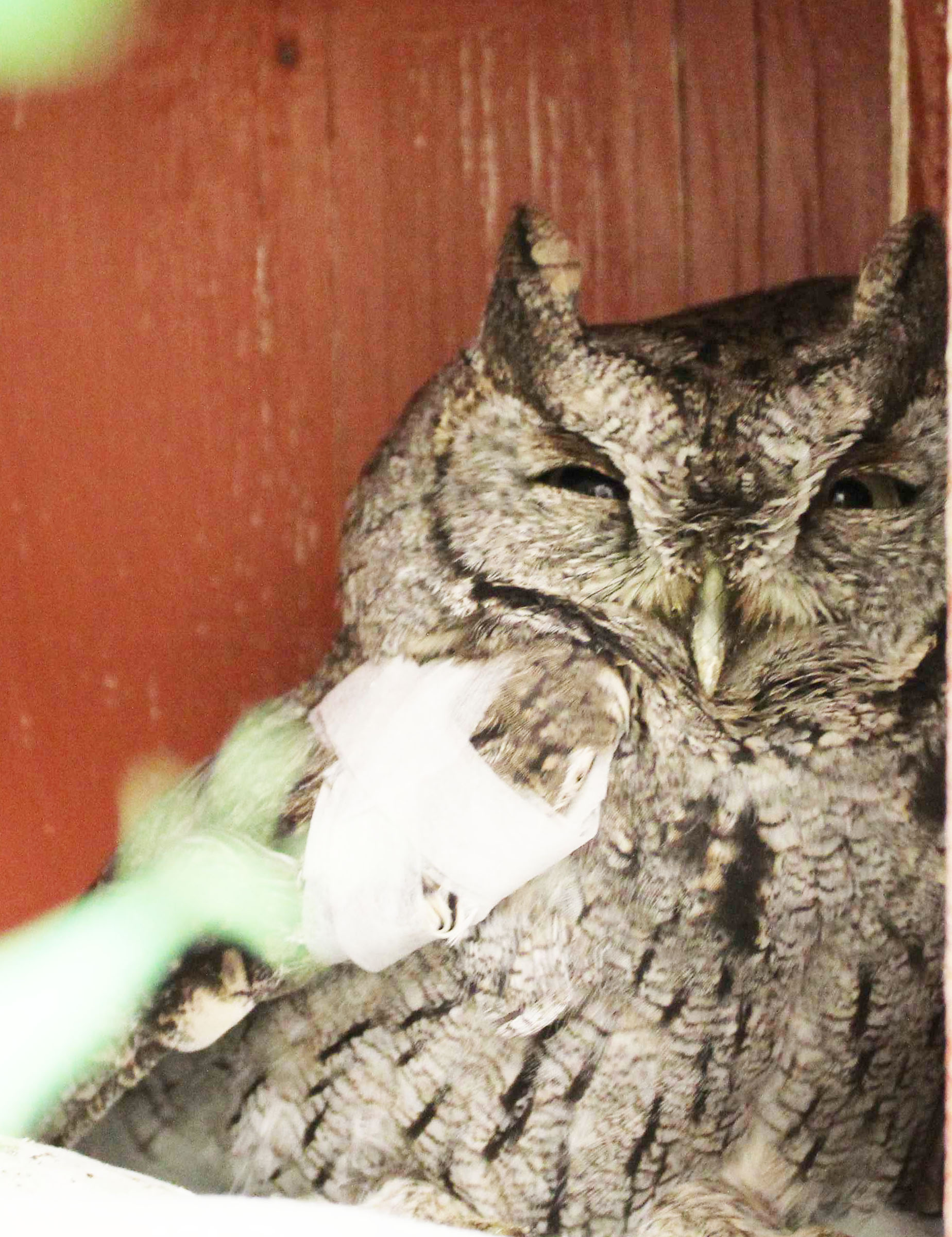

Owls like this Western Screech-Owl are common victims of car collisions
Photo by Cambria Wells
As I drove south on Las Virgenes on the morning of August 18, I passed a very sad sight: three raccoons who had been hit by a car, lying in the road. This was not the first of these incidents I had encountered on my daily drive to work.
Las Virgenes/Malibu Canyon is no stranger to wildlife hit and runs since it is a major artery between the Pacific Coast Highway and the 101. In 2018, it made the news when one of the local mountain lions, P-23, was hit and killed.
According to a study completed by UC Davis, there are 7,000 collisions with wildlife in the State each year, but this study only looked at large species like deer and coyotes. A second research project by Culture Change revealed as many as 400 million animals nationally are killed by vehicles annually, not counting the insects that hit windshields.
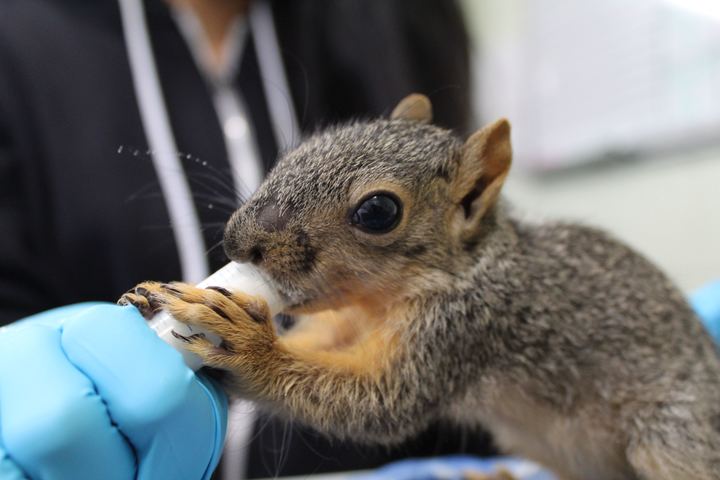
So far this year, California Wildlife Center (CWC) has treated 28 animals who have been hit by cars. The number does not incorporate patients with suspected but unconfirmed auto injuries. These cases include hawks, owls, rabbits, squirrels, coyotes, snakes, opossums, and ducks. Only half have survived due to the severity of their injuries, which may include head trauma, bone fractures, lacerations, soft tissue damage, and internal bleeding.
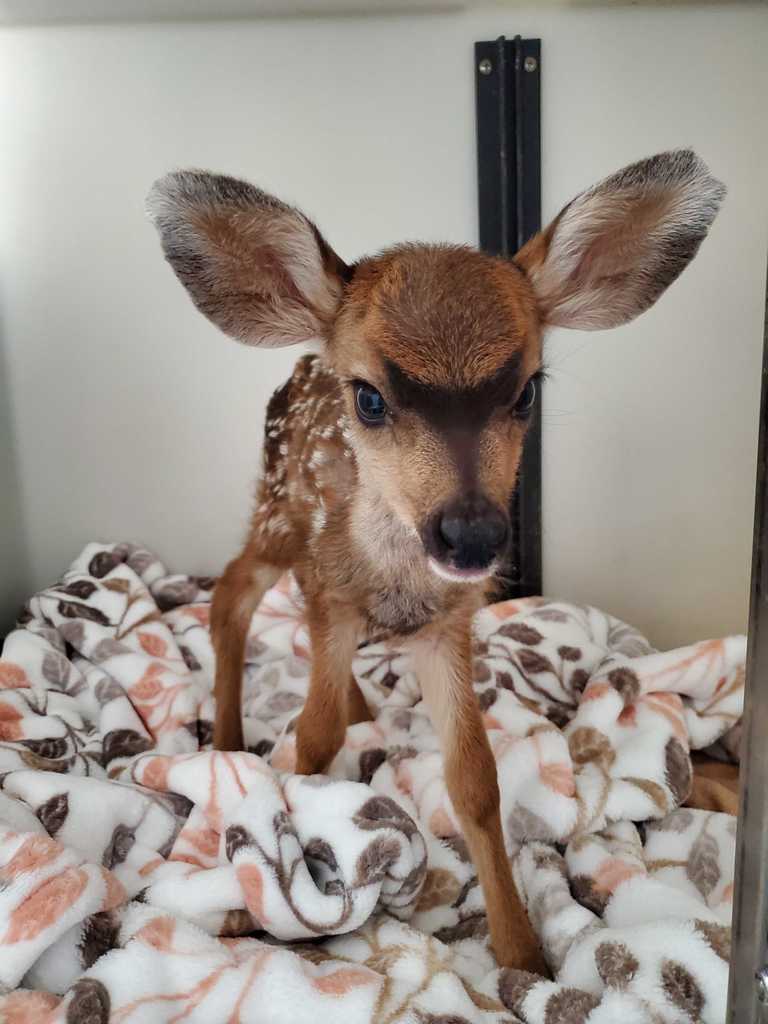

Mule Deer does who are hit by cars in the spring often leave orphaned fawns
Photo by Cambria Wells
One patient, a juvenile Red-Tailed Hawk, was hit by a car on the 101 freeway on February 18. He had suffered a collar bone fracture, a nose abrasion, eye trauma, a wound to his back, and a chest injury. California Wildlife Center staff had to repair this last laceration surgically. The other wounds were treated topically, and the Hawk had to sport a wing bandage while his collar bone healed. After a week, staff noticed the hawk was improving, and two weeks later, he was well enough to move to an outside aviary for physical therapy to regain his strength. A little over a month after he arrived at CWC, the Red-Tailed Hawk returned to the wild. We can only hope he has learned to fly higher over roads and freeways.
The easiest way to prevent unnecessary wildlife injuries and deaths due to automobile collisions is to slow down, especially if you are driving in areas known to have lots of animals such as canyon and mountain roads. Pay attention to road signs that warn about possible crossing locations. Many species are more active at dawn and dusk, so be alert, particularly since the reduced and changing light can make it more difficult to see.
If you hit a wild animal or see one in a collision and they are still alive, contact CWC (310-458-9453), or your local animal control agency for larger animals like deer and coyotes. If you see a deceased wildlife victim of an accident, you can report it to CROS, the California Roadkill Observation System (https://www.wildlifecrossing.net/california/). CROS uses the collected data to inform projects to help reduce wildlife collisions.
If we all slow down and keep our eyes open for wildlife, hopefully, we can reduce these avoidable tragedies.
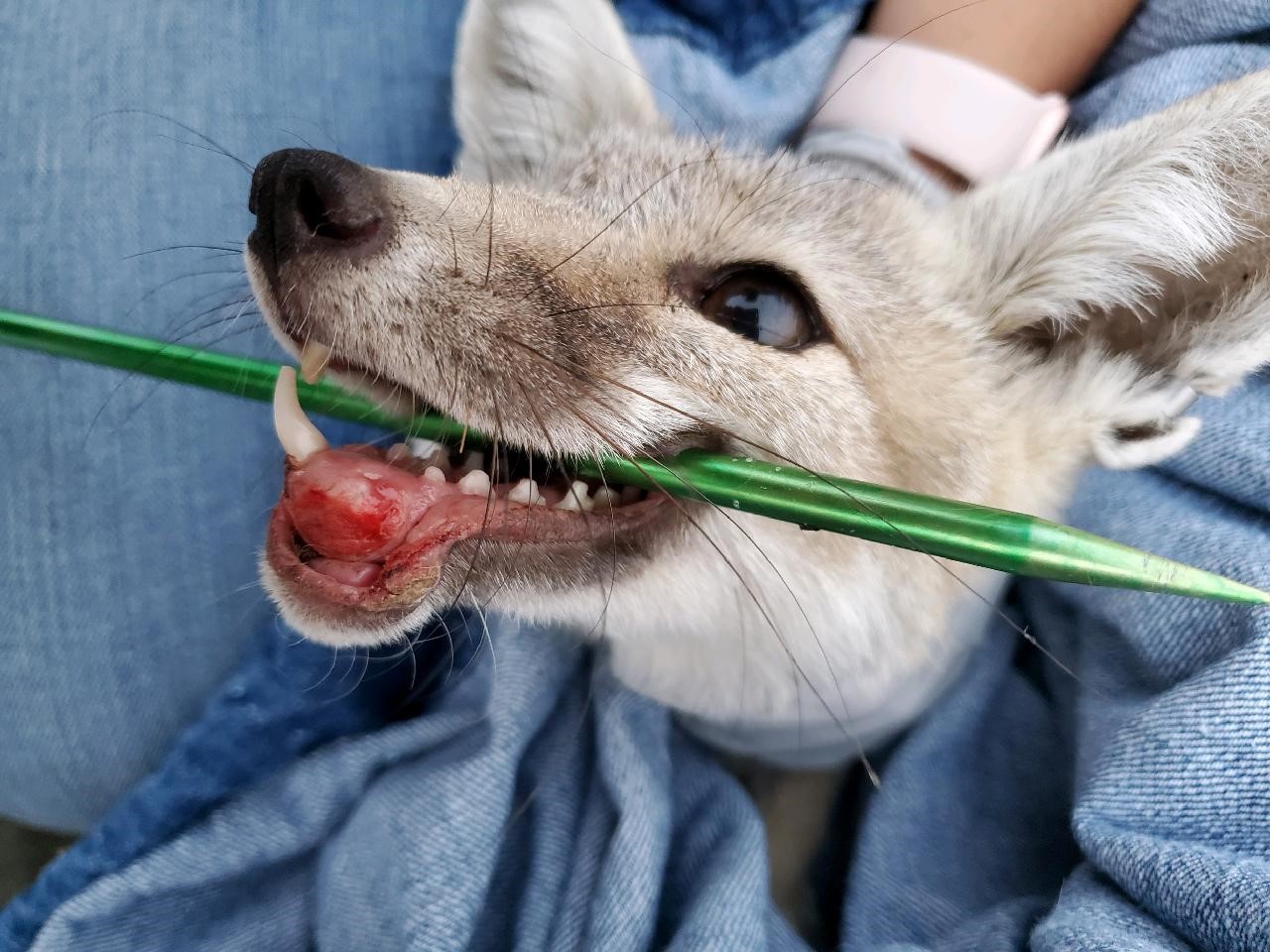
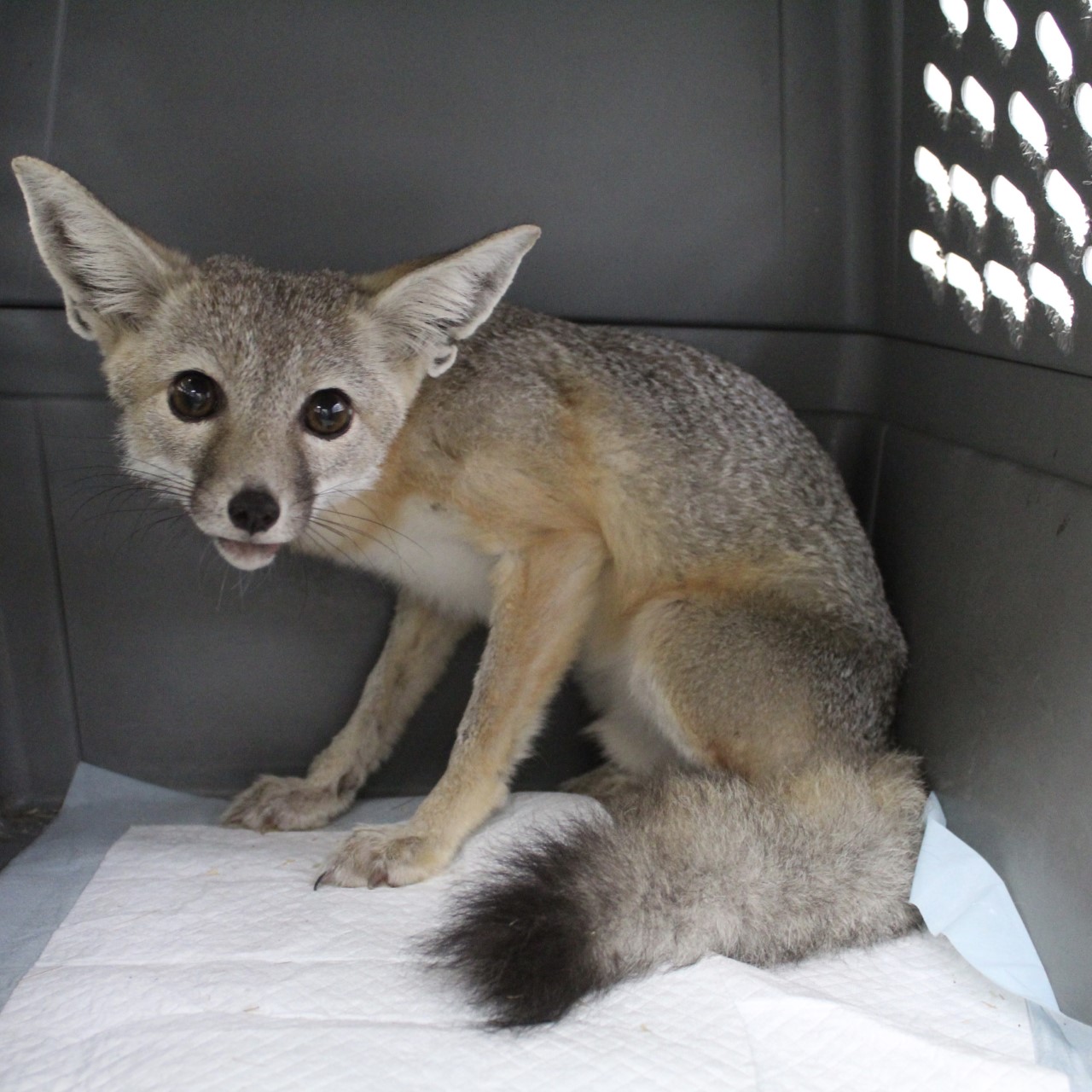








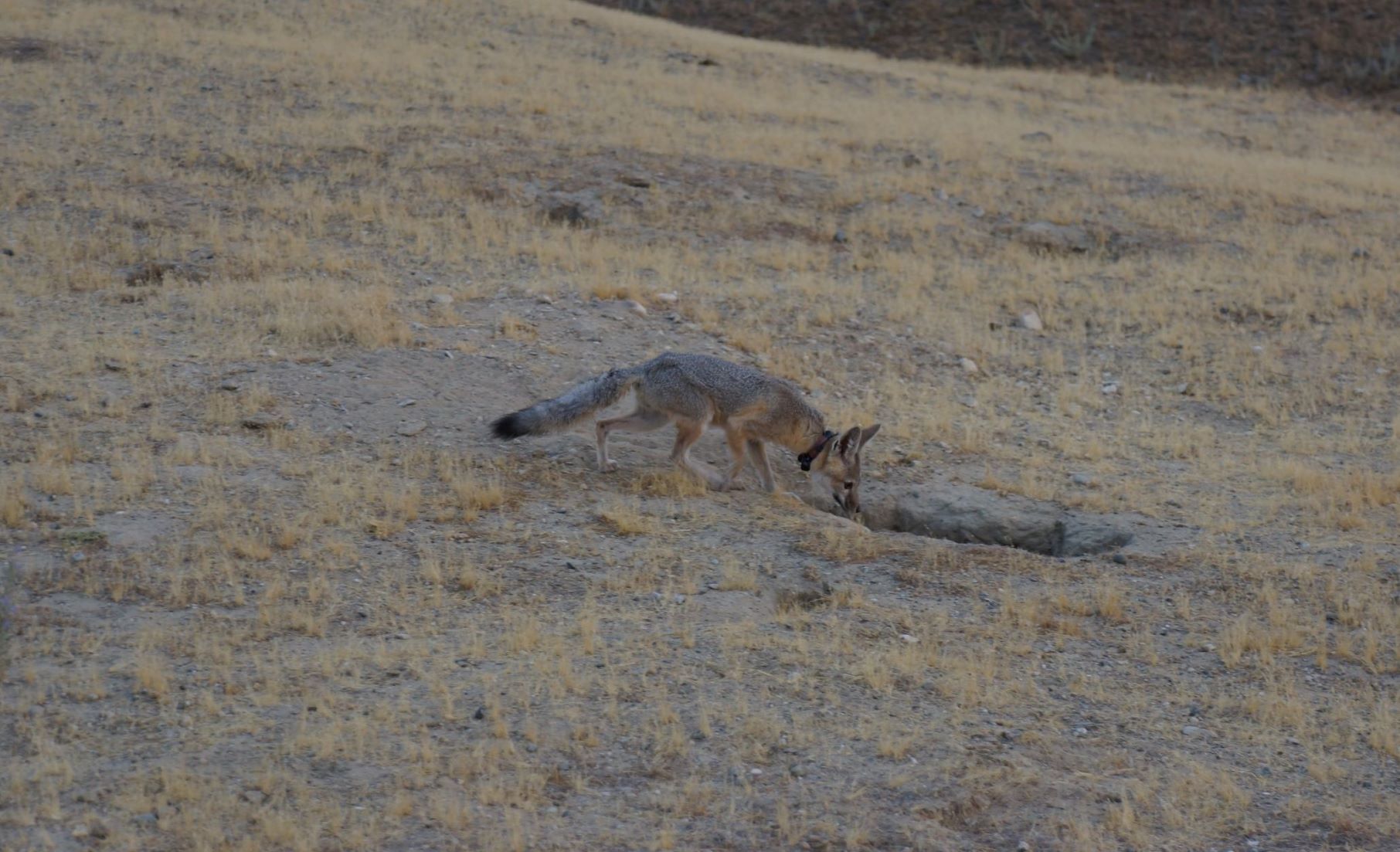
 Directly after the operation, he was taken to CWC for rehabilitation and assigned Wildlife Technician, Cambria Wells, to be his caretaker and monitor his recovery and help him gain some weight back. CDFW and ESRP also wanted to be certain that he could capture his main dietary staple, the kangaroo rat, and that he could fully open his jaw. Over the course of 12 days, we kept a close eye on his sutures, his body weight and body condition, and his demeanor. Luckily for us, he was an easy patient with a quick recovery and a great appetite! During his stay at CWC, we had daily communication with Drs. Pyrdek and Eng, the biologists with ESRP, and CDFW. Their advice was instrumental in his quick recovery!
Directly after the operation, he was taken to CWC for rehabilitation and assigned Wildlife Technician, Cambria Wells, to be his caretaker and monitor his recovery and help him gain some weight back. CDFW and ESRP also wanted to be certain that he could capture his main dietary staple, the kangaroo rat, and that he could fully open his jaw. Over the course of 12 days, we kept a close eye on his sutures, his body weight and body condition, and his demeanor. Luckily for us, he was an easy patient with a quick recovery and a great appetite! During his stay at CWC, we had daily communication with Drs. Pyrdek and Eng, the biologists with ESRP, and CDFW. Their advice was instrumental in his quick recovery!







